About Innopipe
Effective liquids removal of liquids from natural gas streams, above or below ground.
The Problem – gas transmission and distribution systems
Current drip systems are ineffective in removing liquids and contribute to corrosion and black powder formation
Gas transmission pipelines typically use below-grade liquid separators known as “drips”, installed in the pipeline at regular intervals, to collect the liquids carried in a gas stream. These current drips systems are ineffective at transmission velocity gas flow rates because they must allow passage of a tool called a Pipeline Inspection Gauge (“pig”).
These piggable drip designs only capture liquids which flow along the base of the pipe (low velocity stratified flow) while liquids flowing on the outside of the pipe wall (as in high velocity annular flow) would not enter the collection reservoir. As flow rates and velocities are further increased, traditional drips on pipelines are bypassed and conventional separators cannot slow the primary gas stream velocity sufficiently.
In conventional separators or knockouts, the velocity of the gas is reduced all of a sudden when it hits the separator vessel. This rapid slow down causes the liquids in the stream to drop out through gravity but also creates small droplets and mist that is supposed to be removed by the mistex pad or vane in the separator. Often this is not the case and carry over of liquids can occur.
The better way:
The technique in the Innopipe does not require the gas to be slowed down so there is no mist that is carried over once separation happens. The liquid simply moves from the pipe wall into the exterior chamber at the slotted section of the Innopipe as it moves down the pipe. No pressure drop or diameter change to slow the velocity is required.
The Innopipe is not a dehydration unit or a coalescing separator but an efficient liquid removal tool that removes free liquids. Experience shows that very shortly after any liquids have been removed and any mist has formed from a conventional separator or knockout, it recovers very quickly (within 100 feet) and moves to the wall again to form a liquid film again, leaving the middle of the pipe mist and liquid free. We don’t have any data but we have replaced some smaller filter separators in a dry gas system in the past with Innopipe units to keep the dew point within specifications. Once the Mist has recovered and moved to the wall, an Innopipe separator could remove that liquid and would leave that gas drier but we could not provide you with an exact dewpoint number.
Removing free water eliminates most corrosion issues in a wet gas system and would most likely help reduce any black powder problems as well. In most wet systems we have installed two or 3 separators in strategic line locations that knock out the majority of the liquids, and with pigging programs, helps reduce the amount of corrosion. The Innopipe separators are piggable so you can pig a whole system with them in place. Below is a chart of the amount of free liquid that can be removed.
The Solution
Innopipe – Effectively removes 99.5% of liquids from the gas stream
The technology applied with the Innopipe inline gas separator and piggable drip system means it’s both piggable and efficient for liquids separation even at transmission gas velocities.
Innopipe’s patented process uses an annular gas stream separation technique to remove all the liquids without interrupting or changing the flow pattern.
The typical flow in high-pressure natural gas streams is two phase annular flow where liquids flow along the pipe wall and gas travels down the center of the pipe.
The Innopipe system separates the annular flow stream, which contains all the liquids, from the primary gas stream. This secondary gas stream is only approximately 5 % of the primary flow and is directed to a collection reservoir where final separation can occur. The remaining 95 % of the primary gas stream that is inherently liquid-free passes through the separator untouched. The liquids are easily removed from the smaller secondary flow and the cleaned gas is combined and continues downstream.
Advantages
Innopipe system is a cost-effective alternative for natural gas liquids removal
Advantages of Innopipe:
- Can be used in any application where liquids need to be removed from gas streams.
-
Allows unrestricted passage of cleaning and inspection pigs.
-
Used for piggable or non-piggable styles for above and below grade installations.
-
Uses a smaller footprint than conventional separation techniques.
-
Can be installed on pipelines or within natural gas processing systems.
-
Bi-directional capability means costly bypasses and valve arrangements are not needed.
-
Available for both sweet and sour gas applications.
-
Works with low pressure drop (less than 1 psi).
-
More cost-effective than conventional separation techniques, especially on high pressure and large diameter pipelines NPS 24 to NPS 60.
-
Tested in labs and in the field with over 100 installations world-wide.
-
Complete liquids removal significantly reduces risk of pipeline corrosion.
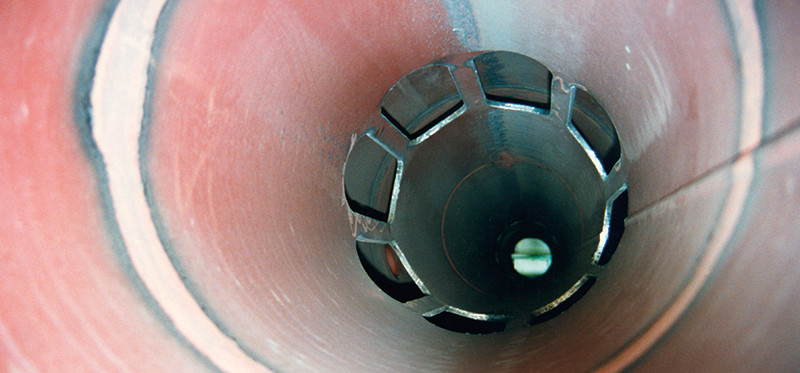
How it works
Innopipe: A two-part system to remove liquids from the gas stream
The Innopipe inline gas separator and piggable drip system has two parts: a flow separator and a collection reservoir. The flow separator uses a pipe the same size as the natural gas line pipe surrounded by a shell to form an annular chamber. The annular chamber is divided into two halves by a pressure tight baffle and each as an inlet/outlet through slotted apertures. The slots are barred to provide support for pigging tools.
From the inlet to the flow separator, the natural gas stream gas is separated into two streams:
- A primary flow of liquids that continues down the internal pipe of the separator, and;
- A secondary flow of gas containing all the liquids in annular flow being drawn into the annular chamber.
Flow separator creates two gas streams
The collection reservoir removes the liquids from the secondary stream by reducing the gas stream velocity and allowing the liquids time to settle out with gravity assistance.
Collection reservoir
The dry secondary stream exits through the collection reservoir nozzle to the separator inlet nozzle. The secondary stream is combined with the primary stream at the downstream slotted aperture. The liquids collected in the reservoir are periodically removed through the blow off piping to an above grade low pressure tank.
Pigging capability is easily achieved by installing isolation valves between the flow separator and the collection reservoir. Closing the valves interrupts the secondary flow and 100 % of the gas stream travels through the center pipe of the flow separator.
Isolation valves help pigging capabilities
The pressure propelling the pig is not allowed to bypass and a pressure differential is maintained. After the pig run is complete the isolation valves are opened for normal operation. The isolation valves can also be used to clean the reservoir off line.

